Acne is a widespread skin concern that affects people across all ages and backgrounds. While conventional treatments are abundant, many individuals seek gentler, nature-based alternatives before turning to chemical-laden solutions. Among the most potent and time-tested herbal remedies are tea tree oil and aloe vera—two botanical powerhouses known for their exceptional ability to soothe inflammation, combat acne-causing bacteria, and promote overall skin balance. These natural ingredients not only target breakouts effectively but also nurture the skin without harsh side effects, making them ideal for those looking to embrace a more holistic skincare approach. By harnessing the power of plant-based solutions, you can achieve clearer, healthier skin the natural way.
In this comprehensive article, we will delve deep into the world of herbal acne solutions. We’ll cover:
- Understanding Acne: Its causes, types, and why herbal remedies can help.
- Tea Tree Oil for Acne: Benefits, usage methods, precautions, and FAQs.
- Aloe Vera for Acne: Healing properties, application tips, and synergy with other remedies.
- Other Top Natural Remedies: A detailed look at popular herbal and home-based treatments such as honey, green tea, chamomile, apple cider vinegar, and more.
- Lifestyle and Dietary Considerations: Why a holistic approach is essential for clear, healthy skin.
- Safety and Patch Testing: How to use herbal solutions safely and effectively.
By the end of this article, you’ll have a well-rounded, in-depth understanding of the best natural ways to tackle acne, along with tips for optimizing your skincare routine in a holistic, sustainable manner.
1. Understanding Acne
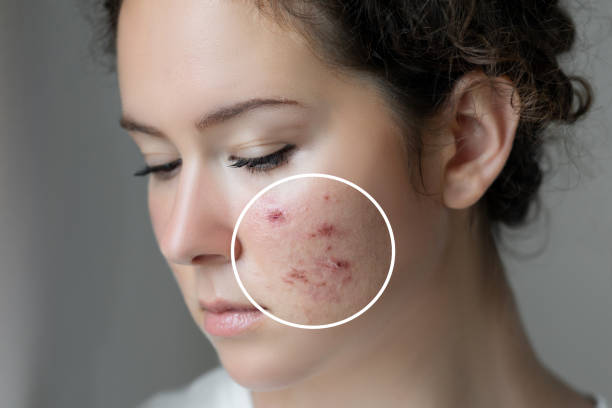
1.1 What Is Acne?
Acne is a skin condition that typically appears when hair follicles become clogged with oil (sebum) and dead skin cells. This buildup can lead to whiteheads, blackheads, pimples, nodules, and cysts. Acne often appears on the face, but it can also manifest on the back, chest, and shoulders. While typically associated with adolescence due to hormonal changes, acne can occur at any stage of life.
1.2 Common Causes of Acne
- Excess Sebum Production
Sebum is a waxy substance that helps protect and hydrate the skin. However, when produced in excess, it can combine with dead skin cells to clog pores. - Hormonal Changes
Fluctuations in hormones—such as those during puberty, menstruation, or pregnancy—can trigger excess oil production, leading to breakouts. - Bacterial Growth
Certain bacteria, such as Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes), thrive in clogged pores. As these bacteria multiply, they cause irritation, redness, and inflammation. - Genetics
A family history of acne can increase your likelihood of experiencing similar skin issues. - Lifestyle Factors
Stress, poor diet, lack of sleep, and certain medications can worsen or trigger acne. Additionally, using inappropriate skincare products can contribute to breakouts. - Environmental Triggers
Pollution, humid conditions, or working in greasy areas (e.g., fast-food kitchens) can exacerbate acne by clogging pores or irritating the skin.
1.3 Why Choose Herbal Remedies?
Many people are drawn to herbal or natural treatments for a variety of reasons:
- Fewer Harsh Chemicals: Conventional acne treatments often contain strong chemicals that can irritate sensitive skin. Herbal remedies tend to be gentler, especially when used correctly.
- Reduced Side Effects: While any product can cause reactions, herbal ingredients generally have a lower risk of severe side effects compared to certain prescription medications.
- Holistic Skincare: Herbal ingredients often promote overall skin health—providing anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and antioxidant benefits that extend beyond just acne treatment.
- Affordability and Accessibility: Many natural remedies can be found in the kitchen or easily sourced from local markets, making them cost-effective and accessible.
2. Tea Tree Oil for Acne

Tea tree oil is derived from the leaves of the Melaleuca alternifolia plant, native to Australia. Known for its potent antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties, tea tree oil has become a go-to herbal solution for acne-prone skin.
2.1 Key Benefits of Tea Tree Oil
- Antibacterial Action
- Tea tree oil is a natural antibacterial agent that effectively fights Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes) and Staphylococcus epidermidis—two bacteria commonly linked to acne. By reducing bacterial growth, it helps prevent breakouts and infections.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects
- The oil’s active component, terpinen-4-ol, possesses strong anti-inflammatory properties, helping to soothe irritated skin, reduce swelling, and calm redness around acne lesions.
- Sebum Regulation
- Tea tree oil may help balance sebum (oil) production, preventing excess oil buildup that clogs pores and triggers acne. This makes it particularly beneficial for people with oily or combination skin.
- Unclogs Pores & Prevents Blackheads
- Its natural cleansing properties help remove dirt, bacteria, and dead skin cells, preventing pore blockages that lead to blackheads and whiteheads.
- Gentle on Skin (When Diluted Properly)
- Compared to harsh chemical treatments, diluted tea tree oil can be less irritating and more suitable for sensitive skin. However, applying it directly without dilution can cause irritation, so always mix it with a carrier oil like jojoba oil, coconut oil, or aloe vera gel.
- Speeds Up Healing & Reduces Acne Scars
- Tea tree oil promotes wound healing by reducing inflammation and encouraging skin regeneration, helping to fade post-acne scars and dark spots over time.
- Fungal & Yeast-Fighting Properties
- Beyond acne, tea tree oil is also effective against fungal acne (Malassezia folliculitis) and yeast-related skin issues, making it a versatile remedy for various skin concerns.
2.2 How to Use Tea Tree Oil for Acne
- Spot Treatment
- Method: Mix 1-2 drops of tea tree oil with a carrier oil (like jojoba oil or sweet almond oil) or water. Using a cotton swab or clean fingertip, apply directly to blemishes.
- Frequency: Start with once a day, then increase to twice daily if your skin tolerates it well.
- DIY Face Mask
- Method: Combine a few drops of tea tree oil with other acne-fighting ingredients such as bentonite clay, honey, or aloe vera gel. Apply the mask to clean skin for 10-15 minutes and rinse with lukewarm water.
- Benefits: Bentonite clay helps to draw out impurities, honey adds antibacterial properties, and aloe vera can soothe inflammation.
- Toner or Facial Mist
- Method: Add 3-5 drops of tea tree oil to 1 cup of distilled water or witch hazel. Transfer the mixture to a spray bottle and shake well. Spritz onto clean skin or apply with a cotton pad.
- Benefits: This toner can help balance the skin’s pH while delivering antibacterial benefits.
- Incorporate into Skincare Products
- Method: If you’re comfortable formulating your own products, you could add a couple of drops of tea tree oil to a moisturizer or serum. However, be cautious and keep the ratio low to avoid irritation.
- Benefits: Enhances the product’s acne-fighting profile without drastically changing its texture or function.
2.3 Precautions and Best Practices
- Perform a Patch Test: Before widespread application, test diluted tea tree oil on a small area of skin (e.g., inside your wrist) to check for sensitivity or allergic reactions.
- Avoid Eye Area: Tea tree oil can cause irritation if it comes into contact with the eyes. Be mindful when applying it near the orbital region.
- Don’t Overdo It: Too frequent or undiluted use can lead to dryness, redness, or irritation. Start slow and adjust usage based on your skin’s response.
- Choose High-Quality Products: Look for 100% pure tea tree oil, preferably from reputable brands that list the concentration of terpinen-4-ol and other active components.
2.4 FAQs: Tea Tree Oil for Acne
- Can I apply tea tree oil directly on pimples without diluting it?
It’s generally advised to dilute tea tree oil in a carrier oil or water to prevent irritation, especially for those with sensitive skin. - How long does it take to see results?
Results vary by individual, but consistent use over a few weeks can yield noticeable improvements. - Can tea tree oil be used for body acne?
Absolutely. Tea tree oil can help reduce breakouts on the back, chest, and shoulders. You might consider using a tea tree oil-infused body wash or spot treatment for these areas.

3. Aloe Vera for Acne

Aloe vera, extracted from the leaves of the aloe plant, is famed for its healing, soothing, and moisturizing properties. Often used to treat sunburns, aloe vera can also be a potent ally in the battle against acne.
3.1 Healing Properties of Aloe Vera
- Anti-Inflammatory
- Aloe vera contains compounds like glycoproteins that help reduce inflammation and swelling, making it highly beneficial for irritated, acne-prone skin.
- Antiseptic and Antibacterial
- Aloe vera’s naturally occurring salicylic acid and sulfur content help fight bacteria, keeping breakouts under control.
- Wound-Healing Abilities
- Acne lesions can sometimes take a while to heal. Aloe vera accelerates cell regeneration and wound healing, which can help reduce the risk of acne scars.
- Hydration Without Clogging Pores
- Unlike heavy creams, aloe vera provides lightweight hydration, suitable for oily and combination skin types that are prone to breakouts.
- pH Balancing
- Aloe vera helps restore the skin’s natural pH, preventing imbalances that can contribute to excessive oil production and breakouts.
- Gentle Exfoliation
- With its natural enzymes and salicylic acid, aloe vera gently removes dead skin cells, preventing clogged pores and promoting a smoother, clearer complexion.
- Rich in Skin-Nourishing Vitamins
- Packed with vitamins A, C, E, and B12, aloe vera provides essential antioxidants that help repair damaged skin, fight free radicals, and promote a more even skin tone.
- Reduces Hyperpigmentation & Dark Spots
- Aloe vera contains aloesin, a compound known to inhibit excess melanin production, helping to fade post-acne marks, dark spots, and uneven skin tone.
- Soothes Sunburn & Skin Sensitivity
- Beyond acne, aloe vera’s cooling and soothing properties help reduce sunburn effects, skin irritation, and redness, making it great for sensitive skin types.
- Supports Collagen Production
- Aloe vera stimulates fibroblasts, the cells responsible for collagen production, helping the skin maintain elasticity and repair itself faster.
3.2 How to Use Aloe Vera for Acne
- Fresh Aloe Gel
- Method: Cut an aloe leaf and scoop out the gel. Apply the gel directly to cleansed skin or specifically on blemishes.
- Benefits: This is the purest form of aloe vera, ensuring maximum benefits without additives.
- Aloe Vera Masks
- Method: Combine aloe vera gel with other skin-friendly ingredients such as turmeric (for its anti-inflammatory properties) or green tea powder (rich in antioxidants). Apply to the face for 15-20 minutes and rinse off gently.
- Tips: Turmeric can stain, so use it sparingly and rinse thoroughly.
- Mix with Tea Tree Oil
- Method: Create a soothing spot treatment by mixing 1 tablespoon of aloe vera gel with 1 drop of tea tree oil. Apply to active acne once or twice daily.
- Benefits: You get the antibacterial punch of tea tree oil with the soothing effect of aloe.
- Over-the-Counter Aloe Vera Gels
- What to Look For: Choose a gel with high aloe vera content (preferably 90% or more) and minimal additives. Many brands include stabilizers and fragrances, which can be irritating.
3.3 Potential Side Effects and Considerations
- Allergic Reactions: Rare but possible. Always perform a patch test if you’ve never used pure aloe before.
- Quality Matters: If using store-bought aloe vera gel, read labels to avoid products with added alcohols, fragrances, or synthetic colorants.
- Storage: Fresh aloe gel can spoil quickly. Store it in the refrigerator in an airtight container, where it can last for about a week.
3.4 FAQs: Aloe Vera for Acne
- Is aloe vera suitable for all skin types?
Generally, yes. Aloe vera is gentle enough for most skin types, including sensitive skin. However, a patch test is recommended for individuals prone to allergies. - Can I leave aloe vera on my face overnight?
Many people find it beneficial to leave aloe vera on overnight as a hydrating mask. However, if you have very sensitive skin, start with shorter applications. - Does aloe vera help fade acne scars?
Aloe vera can assist in the skin’s healing process and may help reduce the appearance of newer, superficial scars. For deeper scars, other targeted treatments or professional procedures may be necessary.

4. Other Top Natural Remedies for Acne

While tea tree oil and aloe vera often take center stage, there is a wide array of other herbal and natural remedies that can offer additional support. Each has unique properties that can help manage acne, reduce inflammation, and promote smoother skin.
4.1 Honey (Especially Manuka Honey)

- Properties and Benefits
- Antibacterial: Manuka honey contains methylglyoxal (MGO), a potent antibacterial compound that helps eliminate acne-causing bacteria like P. acnes.
- Humectant: Honey is a natural humectant, meaning it draws moisture into the skin, keeping it hydrated without clogging pores.
- Wound-Healing: Honey accelerates tissue repair, reducing the risk of acne scars and helping active breakouts heal faster.
- How to Use Honey for Acne
- Spot Treatment: Apply a small dab of honey on active pimples and leave for 20-30 minutes before rinsing.
- Face Mask: Combine honey with cinnamon (a known anti-inflammatory) or apply honey alone for 15-20 minutes. Rinse with warm water.
- Daily Cleanser: Some people use honey as a gentle cleanser, especially for dry or sensitive skin types.
- Precautions
- Allergies: Some people might be allergic to bee products, so always do a patch test.
- Grade of Honey: Not all honey is created equal. Regular supermarket honey may not have the same benefits. Choose raw, unprocessed honey or Manuka honey with a high UMF (Unique Manuka Factor) for best results.

4.2 Green Tea

- Key Components
- Antioxidants: Green tea is rich in catechins, which help fight free radicals and reduce inflammation.
- Regulates Sebum Production: Some studies suggest topical green tea extracts can help balance oil production and educing the risk of clogged pores and breakouts.
- Anti-Inflammatory & Soothing: The polyphenols in green tea help calm redness, swelling, and irritation.
- Topical Application
- Green Tea Compress: Brew a cup of green tea, let it cool, and use a cotton pad to apply it to the skin.
- Face Mask: Mix cooled green tea or green tea powder with aloe vera gel or honey to create a soothing mask.
- Drinking Green Tea for Internal Benefits
- Detoxifies the Skin: Green tea helps flush out toxins and reduce inflammation from within.
- Hormonal Balance: Some studies suggest drinking green tea daily may help regulate hormonal acne.

4.3 Chamomile

- Properties
- Soothing: Chamomile’s anti-inflammatory properties can help reduce redness and irritation.
- Gentle: Known as a calming herb, chamomile is less likely to irritate sensitive skin.
- Natural Skin Brightener: Chamomile can fade dark spots and acne scars over time.
- Ways to Use Chamomile
- Chamomile Toner: Brew chamomile tea, let it cool, and apply it to the face as a soothing toner.
- Chamomile Compress: Place cooled chamomile tea bags on inflamed pimples or irritated areas.
- Precautions
- Allergies: Chamomile is part of the daisy family (Asteraceae). Individuals allergic to daisies, ragweed, or chrysanthemums should proceed with caution (if you’re allergic to these patch test first).

4.4 Apple Cider Vinegar (ACV)

- Acidic Properties
- pH Balancer: ACV can help restore the skin’s natural pH, creating an environment less conducive to bacterial overgrowth.
- Mild Exfoliation: Contains acetic acid & malic acid, which gently remove dead skin cells, unclogging pores.
- How to Use ACV for Acne
- Diluted Toner: Mix 1 part ACV with 3-4 parts water, depending on your skin’s sensitivity. Apply with a cotton pad after cleansing.
- Spot Treatment: Dab the diluted solution on individual pimples and let it dry.
- Potential Side Effects
- Irritation or Burns: Applying undiluted ACV can cause skin irritation or even chemical burns. Always dilute.
- Strong Smell: ACV has a pungent smell, but it dissipates as it dries.

4.5 Witch Hazel

- Astringent Properties
- Tannins: Witch hazel contains tannins that help tighten pores and reduce excess oil production.
- Anti-Inflammatory: Can soothe inflamed or irritated skin.
- Usage
- Toner: Apply alcohol-free witch hazel with a cotton pad after cleansing.
- Combination with Essential Oils: Enhance witch hazel’s benefits by adding a drop of tea tree oil or lavender oil.
- Cautions
- Potential Dryness: Witch hazel can be drying for some individuals. Moisturize afterward.
- Alcohol-Free Formulations: Choose an alcohol-free witch hazel to reduce the risk of irritation.

4.6 Turmeric

- Active Ingredient
- Curcumin: A powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant compound that helps reduce acne flare-ups.
- Fades Dark Spots & Scars: Turmeric inhibits melanin production, helping lighten post-acne marks.
- Turmeric Masks
- Simple Paste: Mix turmeric powder with a small amount of water or aloe vera to form a paste. Apply for 10-15 minutes.
- With Yogurt or Honey: Combine turmeric with yogurt (for probiotics) or honey (for antibacterial action).
- Staining Concerns
- Skin Discoloration: Turmeric can leave a temporary yellow stain on the skin. Use small amounts and rinse thoroughly.
- Fabric Staining: Protect your clothing and surfaces.

4.7 Neem

- Medicinal Properties
- Antibacterial and Antifungal: Neem’s active compounds help fight the bacteria that cause acne.
- Purifying: Popular in Ayurvedic medicine, neem is believed to purify the blood and skin and also prevent new breakouts.
- Neem for Acne
- Neem Oil: Dilute with a carrier oil to apply as a spot treatment.
- Neem Leaf Paste: Blend fresh neem leaves with water or aloe vera gel to form a paste and apply as a face mask.
- Odor and Irritation
- Strong Smell: Neem has a distinct, bitter smell.
- Patch Test: As with all herbal products, do a patch test, as neem can irritate sensitive skin.

4.8 Essential Oils (Beyond Tea Tree)

- Lavender Oil
- Calming Properties: Helps reduce redness and irritation.
- How to Use: Dilute with a carrier oil and apply to the affected area.
- Rosemary Oil
- Antimicrobial: Can help control bacterial growth on the skin.
- Usage: Perfect for mixing in a moisturizer or toner, ensuring proper dilution.
- Cedarwood Oil
- Skin-Balancing: Known to help regulate sebum production.
- Precautions: Always patch test and never apply essential oils directly on the skin without dilution.

5. Lifestyle and Dietary Considerations

Natural topical remedies work best when combined with a holistic approach to health. Incorporating positive lifestyle changes and paying attention to your diet can significantly enhance the effectiveness of herbal acne treatments.
5.1 Diet and Hydration
- Reduce High-Glycemic Foods
- Examples: Sugary snacks, white bread, and processed cereals can spike blood sugar, which may exacerbate acne.
- Alternative: Opt for whole grains, legumes, and vegetables.
- Increase Fruit and Vegetable Intake
- Antioxidants: Produce like berries, leafy greens, and colorful vegetables provide vitamins and antioxidants that help maintain healthy skin.
- Fiber: Supports digestion and may aid in regulating hormones.
- Limit Dairy and High-Saturated Fats
- Why: Some studies suggest a possible link between dairy consumption and acne severity.
- Healthy Fats: Incorporate avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil for balanced fat intake.
- Stay Hydrated
- Daily Intake: Aim for at least 8 glasses of water per day (about 2 liters), adjusting for activity levels and climate.
- Herbal Teas: Consider adding green tea, chamomile, or spearmint tea to your routine for added skin benefits.
5.2 Stress Management
- Stress and Cortisol
- Hormonal Impact: Elevated cortisol levels can trigger excess oil production, leading to breakouts.
- Techniques: Practice meditation, yoga, or breathing exercises to regulate stress.
- Adequate Sleep
- Skin Regeneration: The body repairs itself during sleep, making 7-9 hours per night essential for healthy skin.
- Melatonin Production: Adequate rest supports melatonin levels, which can have a protective effect on the skin.
5.3 Exercise and Movement
- Improved Circulation
- Benefit: Regular exercise promotes blood flow, delivering nutrients to the skin and aiding in waste removal.
- Sweating: Helps purge pores of toxins, though it’s crucial to shower or cleanse the skin soon after to prevent pore-clogging.
- Balanced Hormones
- Effects: Exercise can help regulate hormones, reducing acne flare-ups.
- Low-Intensity vs. High-Intensity: Both can be beneficial; choose an exercise regime that aligns with your fitness level.
5.4 Skincare Habits
- Choose Non-Comedogenic Products
- Reason: These formulations are designed not to clog pores, reducing the risk of breakouts.
- Labels: Look for terms like “oil-free,” “won’t clog pores,” or “non-comedogenic.”
- Regular Cleansing
- Best Practice: Wash your face twice a day with a gentle cleanser to remove dirt, oil, and makeup.
- Post-Workout: Always cleanse after heavy sweating to avoid trapped bacteria and sebum in pores.
- Avoid Over-Exfoliation
- Risk: Too much exfoliation can strip the skin’s natural barrier, causing irritation and more breakouts.
- Optimal Frequency: 1-2 times a week, depending on your skin type, with a gentle scrub or a mild chemical exfoliant.
- No Picking or Popping
- Why: Popping pimples can introduce more bacteria, worsen inflammation, and potentially cause scarring.
- Alternative: Use a targeted spot treatment or consult a dermatologist for extraction.
6. Safety and Patch Testing

While herbal remedies can be gentler than some traditional acne medications, it’s still important to take precautions to protect your skin.
6.1 Patch Testing
- Why Patch Test?
- Prevention: Identify allergic reactions or irritations before applying a product to the entire face.
- Areas to Test: Common places include the inside of the wrist, behind the ear, or a small spot on the jawline.
- How to Patch Test
- Method: Apply a small amount of the remedy and wait 24 hours.
- What to Look For: Redness, itching, burning, swelling, or any adverse reaction indicates you should discontinue use.
6.2 When to Seek Professional Help
- Persistent or Severe Acne
- Reason: Cystic acne or widespread inflammation may require prescription-strength treatments or professional advice.
- Dermatologist Consultation: A dermatologist can recommend specialized medication or in-office treatments like chemical peels, light therapy, or extraction.
- Signs of Infection
- Indicators: Painful, swollen nodules or pustules that seem to be spreading.
- Action: Consult a healthcare provider promptly to prevent complications.
- Unexpected Reactions
- Allergy: Severe rash, hives, or breathing difficulties should be treated as a medical emergency.
- Interference with Medications: If you take prescription medicines, always consult your doctor before starting any new herbal regimen.
7. Putting It All Together: A Sample Herbal Acne Routine

Below is a sample routine incorporating some of the top herbal acne solutions discussed, alongside lifestyle habits that can enhance your results. Feel free to adjust based on your skin type, schedule, and specific needs.
- Morning Routine
- Cleanse: Use a gentle, non-comedogenic cleanser with soothing ingredients like chamomile or green tea extract.
- Tone: Spritz or apply a diluted tea tree oil or witch hazel toner to balance pH and add antibacterial properties.
- Moisturize: Opt for a lightweight moisturizer, possibly infused with aloe vera for hydration.
- Sun Protection: Use an oil-free sunscreen (SPF 30 or higher) to prevent UV damage and reduce hyperpigmentation.
- Evening Routine
- Cleanse: Remove makeup and impurities with a mild cleanser. Double-cleanse if you wore heavy makeup.
- Spot Treatment: Apply diluted tea tree oil or aloe vera gel directly onto blemishes.
- Optional Mask (1-2 times a week): Use a clay mask with a drop of tea tree oil or a honey-turmeric mask to target acne and soothe inflammation.
- Moisturize: Finish with a calming moisturizer, ensuring skin stays hydrated overnight.
- Weekly Extras
- Gentle Exfoliation: A mild scrub or a chemical exfoliant like salicylic acid once a week to slough off dead skin cells.
- Steam Treatment: Occasionally steam your face with herbs like chamomile or rosemary to open pores and aid in deep cleansing.
- Lifestyle Maintenance
- Hydration: Drink adequate water and consider herbal teas for additional antioxidant support.
- Balanced Diet: Emphasize whole foods, vegetables, and fruits, limiting high-sugar or highly processed foods.
- Stress Management: Incorporate relaxation techniques or exercise to keep cortisol levels in check.
8. Conclusion: Achieving Clear Skin Naturally
Harness the power of nature with herbal acne solutions like tea tree oil, aloe vera, and other potent botanicals—honey, green tea, chamomile, apple cider vinegar, witch hazel, turmeric, and neem. These natural remedies offer soothing, antibacterial, and anti-inflammatory benefits to help combat breakouts while being gentle on your skin.
For lasting results, consistency is key! Pair these herbal treatments with a healthy lifestyle—nourishing foods, hydration, stress management, and a solid skincare routine—to unlock clear, glowing skin. Remember, every skin type is unique, so listen to yours and introduce new remedies mindfully.
Ready for more expert herbal skincare tips? Explore the wonders of nature at aayushii.com and elevate your skincare game today!
Quick Reference Checklist
- Tea Tree Oil: Dilute properly; best used as a spot treatment or in masks.
- Aloe Vera: Fresh gel is ideal; soothes inflammation and helps with wound healing.
- Honey (Manuka): Antibacterial; excellent for masks and spot treatments.
- Green Tea: Use as a toner or in masks; rich in antioxidants.
- Chamomile: Calming toner; great for sensitive, inflamed skin.
- Apple Cider Vinegar: Always dilute before applying; balances pH and gently exfoliates.
- Witch Hazel: Astringent properties; opt for alcohol-free versions to minimize dryness.
- Turmeric: Potent anti-inflammatory; be mindful of staining.
- Neem: Powerful antibacterial; can be used as oil or leaf paste.
- Lifestyle: Balanced diet, good hydration, stress reduction, and consistent skincare
By following these guidelines and incorporating herbal solutions into your routine, you can give your skin the best chance to heal, regenerate, and glow with natural radiance.
FAQs: About Herbal Acne Solutions
Do natural remedies work as quickly as prescription medications?
Herbal remedies often need consistent use over a longer period to show visible results. While they can be highly effective, patience and persistence are key.
Can I use multiple herbal remedies at once?
Yes, but proceed cautiously. Combining too many active ingredients (e.g., tea tree oil, salicylic acid, and retinol) can overwhelm the skin, leading to irritation or dryness. Introduce new products gradually.
Are these remedies safe during pregnancy?
Many herbal remedies are generally considered safe, but pregnancy involves unique hormonal and sensitivity changes. Always consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice.
Is it necessary to change my diet if I use herbal remedies?
While not mandatory, a balanced diet can significantly improve skin health and amplify the benefits of topical treatments.
Can I store DIY remedies for later use?
Most DIY remedies, especially those containing fresh ingredients like aloe vera, are best used immediately or stored in the fridge for short durations. This reduces the risk of bacterial growth.
Are herbal solutions enough to eliminate acne scars?
Natural remedies can help fade minor scars over time and support overall skin health, but more severe scarring may require professional treatments like microdermabrasion, chemical peels, or laser therapy.
How long should I wait to see improvements in my acne?
Depending on the severity of your acne and your skin’s unique characteristics, noticeable improvements can take anywhere from a few weeks to a couple of months.





