Acne scars can be a frustrating reminder of past breakouts, but you don’t have to live with them. With the right over-the-counter products and consistent skincare, you can effectively reduce acne scars and improve your skin’s overall texture. This guide will delve into the science behind acne scar formation, the most effective OTC ingredients to target different types of scars, and how to create a personalized skincare routine to achieve clearer, more radiant skin.
Understanding Acne Scars
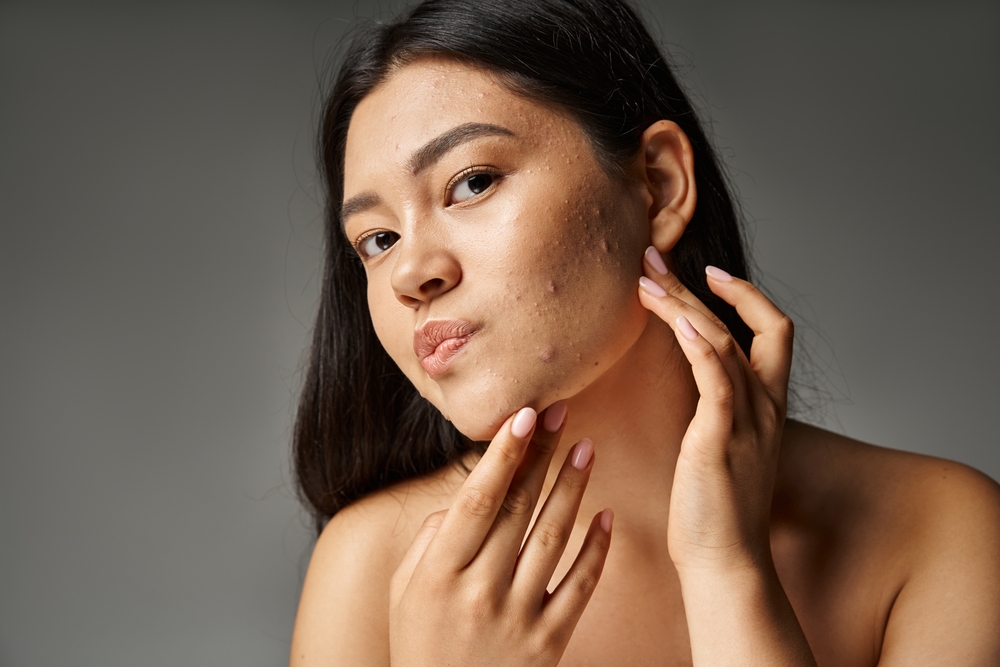

Acne scars are the result of inflammation within the dermis caused by acne, and they occur when the skin attempts to heal itself but doesn’t fully restore its original texture and appearance. Understanding the types and causes of acne scars can help in determining the most effective treatment options.
Types of Acne Scars
- Atrophic Scars: These are the most common and occur when there is a loss of tissue.
- Ice Pick Scars: Narrow, deep pits that extend into the dermis.
- Boxcar Scars: Broad, rectangular depressions with sharp edges.
- Rolling Scars: Undulating scars with sloped edges, giving the skin a wavy texture.
- Hypertrophic or Keloid Scars: Raised scars caused by an overproduction of collagen during the healing process. Keloid scars can grow beyond the boundaries of the original acne site.
- Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH): Not a true scar but a discoloration that occurs after acne has healed. It is more common in darker skin tones and can fade over time.
Causes of Acne Scars
- Severe Inflammation: More intense acne can cause significant damage to the skin.
- Delay in Treatment: Prolonged acne increases the likelihood of scarring.
- Picking or Squeezing Acne: This can worsen inflammation and increase the risk of scarring.
- Genetics: A family history of acne scarring can make individuals more susceptible.
Prevention of Acne Scars
- Early Treatment: Addressing acne promptly with appropriate medication or therapies.
- Avoid Picking: Refrain from squeezing or picking at pimples.
- Sun Protection: Using sunscreen to prevent hyperpigmentation and help scars heal better.
Treatment Options
- Topical Treatments:
- Retinoids and other products to promote cell turnover.
- Silicone gels for raised scars.
- Procedures:
- Chemical Peels: To remove the top layer of skin and improve texture.
- Microneedling: Stimulates collagen production.
- Laser Therapy: Resurfaces the skin and reduces scar visibility.
- Dermal Fillers: Used for deep scars like boxcar or rolling scars.
- Subcision: Releases fibrous bands pulling the skin down in atrophic scars.
- Home Remedies: Ingredients like aloe vera, honey, or tea tree oil may help with mild discoloration or texture issues but are less effective on deep scars.
Understanding the types of acne scars you have is the first step to finding the right treatment plan. Consult a dermatologist for personalized advice and interventions tailored to your skin type and scarring.
Key Ingredients for Reducing Acne Scars
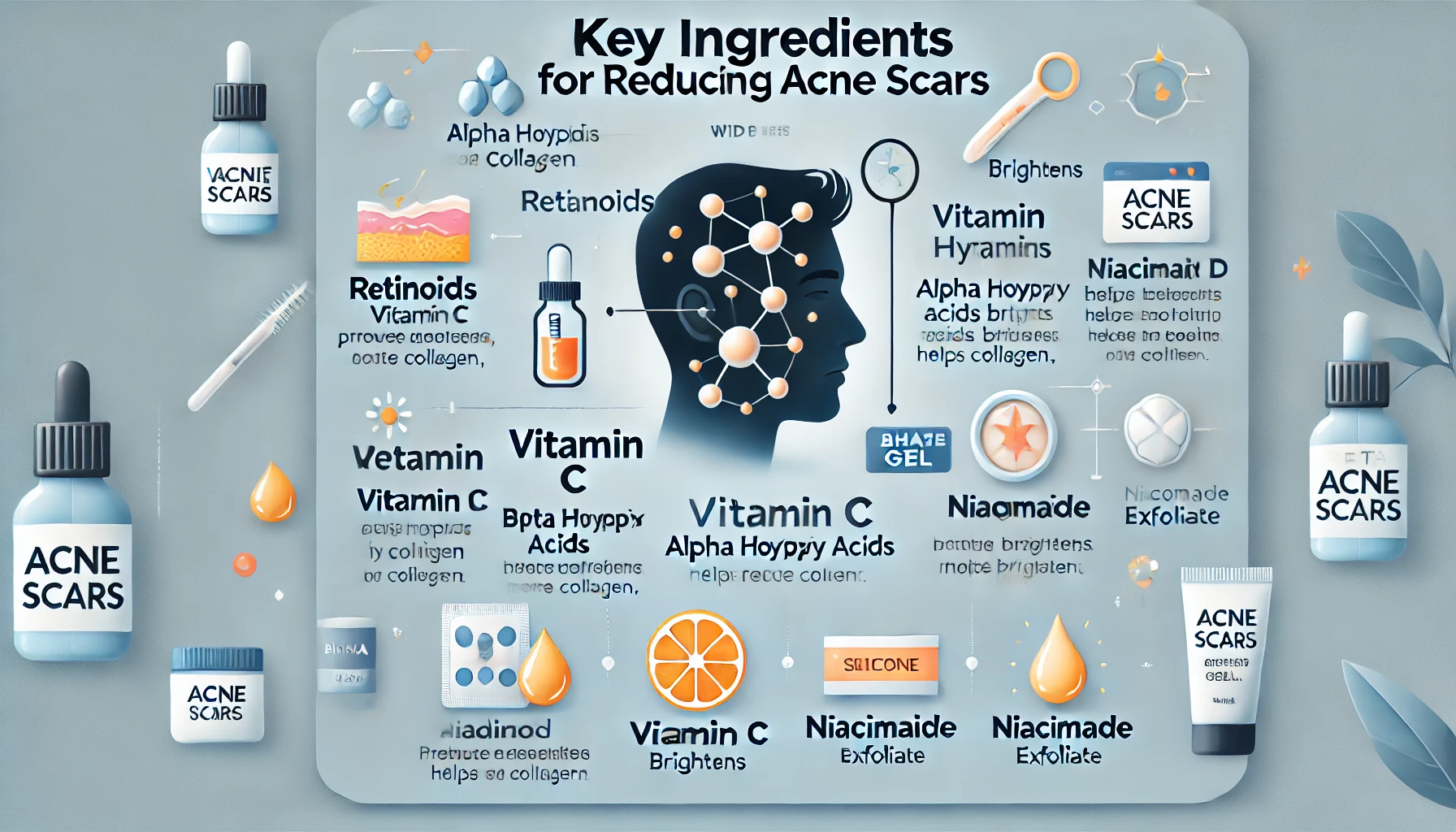
Science-based skincare revolves around active ingredients that target scar tissue and support skin regeneration. Here are some of the most effective ones:
1. Retinoids (Retinol and Adapalene)
Retinoids are derivatives of Vitamin A that promote cell turnover and stimulate collagen production. They are highly effective for:
- Smoothing uneven texture.
- Fading post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH).
- Encouraging new, healthy skin growth.
Product Recommendation: Look for products containing retinol or adapalene (e.g., Differin Gel) for nightly use. Start with a low concentration to minimize irritation.
2. Alpha Hydroxy Acids (AHAs)
AHAs, such as glycolic acid and lactic acid, are chemical exfoliants that remove dead skin cells and encourage new skin formation. These acids are ideal for:
- Reducing the appearance of shallow scars.
- Brightening dark spots.
Product Recommendation: Choose glycolic acid serums or peels with concentrations between 5% and 10%, like The Ordinary Glycolic Acid 7% Toning Solution.
3. Beta Hydroxy Acids (BHAs)
Salicylic acid, the most common BHA, penetrates deep into pores to exfoliate and unclog them. It’s beneficial for:
- Reducing active acne to prevent further scarring.
- Minimizing discoloration and improving skin texture.
Product Recommendation: Use salicylic acid-based toners or cleansers, such as Paula’s Choice Skin Perfecting 2% BHA Liquid Exfoliant.
4. Niacinamide
Niacinamide, a form of Vitamin B3, is a versatile ingredient that reduces inflammation and strengthens the skin’s barrier. It helps with:
- Fading hyperpigmentation.
- Reducing redness and irritation.
- Improving skin elasticity.
Product Recommendation: Incorporate niacinamide serums like The Ordinary Niacinamide 10% + Zinc 1% into your daily routine.
5. Vitamin C
Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that brightens the skin and promotes collagen synthesis. It’s particularly effective for:
- Lightening dark scars.
- Enhancing overall skin radiance.
Product Recommendation: Opt for daytime use serums containing L-ascorbic acid (e.g., SkinCeuticals C E Ferulic).
6. Silicone Gel or Patches
Silicone helps hydrate and flatten raised scars by creating a protective barrier over the skin. It’s especially useful for:
- Softening hypertrophic scars.
- Preventing further scar thickening.
Product Recommendation: Try silicone sheets or gels like Scar Away Silicone Scar Gel for targeted treatment.
7. Azelaic Acid
Azelaic acid is a naturally occurring compound that reduces inflammation and pigmentation. It’s effective for:
- Treating PIH and melasma.
- Enhancing skin texture.
Product Recommendation: Use azelaic acid creams, such as The Ordinary Azelaic Acid Suspension 10%.
Best Practices for Using Over-the-Counter (OTC) Products

Taking a mindful and measured approach when incorporating OTC skincare products into your routine is essential to maximize benefits and minimize potential side effects. Here’s an expanded explanation of each best practice:
1. Start Slow
When beginning a new skincare regimen, it’s crucial to introduce only one active ingredient at a time. Many OTC products contain potent ingredients like salicylic acid, benzoyl peroxide, or retinoids that can be effective but also irritating if overused.
- Why: Your skin needs time to adapt to these new substances. Adding too many products at once increases the risk of irritation, redness, or peeling.
- How: Start with a small amount, applying every other day or as directed, and gradually increase usage as your skin tolerates it.
2. Patch Test
Always test new products on a small, inconspicuous area of your skin (such as behind the ear or on the inner forearm) before applying them to your entire face.
- Why: A patch test helps you identify any allergic reactions or irritation before exposing a larger area of your skin.
- How: Apply the product to the test area and wait 24–48 hours to check for redness, itching, or swelling. If no adverse reaction occurs, proceed with full application.
3. Use Sunscreen
Daily sunscreen application is non-negotiable, especially when using products with active ingredients like AHAs, BHAs, or retinoids, which can make your skin more sensitive to the sun.
- Why: UV exposure can exacerbate hyperpigmentation, slow scar healing, and reduce the efficacy of treatments. Unprotected exposure might also lead to premature aging and increase the risk of skin cancer.
- How: Opt for a broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher, and reapply every two hours if outdoors. Choose a non-comedogenic formula if you have acne-prone skin.
4. Be Consistent
Skincare is a marathon, not a sprint. OTC products often take several weeks to months to show visible improvements.
- Why: Skin turnover cycles (typically 28 days for most people) mean that results aren’t immediate. Long-term consistency ensures you see the product’s full benefits.
- How: Stick to a routine, applying products as instructed (e.g., once or twice daily). Keep a journal or take progress photos to track changes.
5. Moisturize
Maintaining your skin’s natural barrier with a good moisturizer is key, especially when using products that may dry or irritate your skin, like acne treatments.
- Why: A healthy skin barrier reduces irritation, prevents transepidermal water loss, and enhances the effectiveness of active ingredients. Dehydrated or compromised skin is more prone to inflammation and sensitivity.
- How: Use a non-comedogenic moisturizer to ensure it doesn’t clog pores. Look for ingredients like hyaluronic acid, ceramides, or glycerin to hydrate and strengthen your skin.
By following these best practices, you can create a safe and effective skincare routine tailored to your skin’s needs, reducing the likelihood of irritation while achieving your desired results.
Step-by-Step Skincare Routine for Acne Scars

Here’s a simple routine incorporating OTC products for scar treatment:
Morning Routine:
- Cleanser: Use a gentle cleanser to remove impurities.
- Toner/Exfoliant: Apply a mild exfoliant containing glycolic or salicylic acid.
- Serum: Use a Vitamin C serum to brighten and protect the skin.
- Moisturizer: Apply a lightweight, hydrating moisturizer.
- Sunscreen: Use a broad-spectrum SPF 30 or higher.
Evening Routine:
- Cleanser: Wash your face with a gentle cleanser.
- Toner: Use a niacinamide-based toner for calming and hydration.
- Treatment: Apply a retinoid or azelaic acid cream.
- Moisturizer: Finish with a nourishing moisturizer to lock in hydration.
When to See a Dermatologist
OTC products are effective for mild to moderate acne scars, but more severe cases may require professional treatments like:
Microneedling
- What It Is: A minimally invasive procedure that uses fine needles to create controlled micro-injuries in the skin. This stimulates collagen and elastin production, improving the texture and appearance of atrophic scars (e.g., rolling scars).
- Benefits: Smooths skin texture over time with minimal downtime.
Chemical Peels
- What It Is: A professional-grade exfoliation treatment that removes damaged outer skin layers, promoting new skin growth. Stronger peels than those available OTC are used to treat more stubborn scars.
- Benefits: Reduces discoloration, improves texture, and softens scars with repeated sessions.
Laser Therapy
- What It Is: Lasers (such as fractional CO2 or erbium lasers) target deeper layers of the skin, promoting skin remodeling and collagen production.
- Benefits: Particularly effective for deep scars and extensive scarring. Results can be dramatic with multiple sessions.
Subcision
- What It Is: A minor surgical procedure where a needle is inserted under the skin to break up fibrous bands pulling down the surface, common in rolling scars.
- Benefits: Releases scar tissue to create a smoother appearance.
Dermal Fillers
- What It Is: Injectable fillers are used to “fill in” deep scars, like boxcar scars, to even out the skin surface.
- Benefits: Provides immediate results, although temporary (lasting several months to a year).
Steroid Injections
- What It Is: Injections of corticosteroids directly into hypertrophic or keloid scars to flatten and soften them.
- Benefits: Reduces raised scars over time, often in conjunction with other therapies.
- Microneedling: Promotes collagen production to reduce indentations.
- Chemical Peels: Provides deeper exfoliation for stubborn scars.
- Laser Therapy: Targets deeper layers of skin for significant scar reduction.
Consult a dermatologist if you don’t see improvements after 3–6 months of consistent OTC treatment.
Conclusion
Reducing acne scars is achievable with the right combination of over-the-counter products and a diligent skincare routine. By incorporating science-backed ingredients like retinoids, AHAs, and Vitamin C, you can gradually fade scars and improve your skin’s texture and tone. Remember, patience and consistency are key to achieving noticeable results.
For more skincare tips and product recommendations, visit aayushii.com, your trusted source for all things skincare!
FAQ: Effective Ways to Reduce Acne Scars with Over-the-Counter Products
1. Do OTC products help reduce acne scars?
Yes, OTC products with ingredients like retinoids, AHAs, and Vitamin C can help fade scars and improve skin texture over time.
2. How long before I see results from OTC treatments?
It usually takes 8–12 weeks of consistent use to see noticeable improvements.
3. Can OTC products work on all skin types?
Most OTC products are safe, but it’s important to choose the right one for your skin type. Patch test before full application.
4. Should I use OTC products if I still have acne?
Yes, some OTC treatments can treat both acne and scars, but avoid overusing harsh products.
5. Is sunscreen necessary when treating acne scars?
Yes, sunscreen is crucial to protect skin from UV damage, which can worsen scars.
6. What if OTC products don’t work?
If there’s no improvement after 3–6 months, consult a dermatologist for more advanced treatments.
7. Can OTC products prevent new scars?
Yes, by treating acne early and promoting healing, OTC products can help prevent new scars.
8. What’s the best skincare routine for acne scars?
Use a gentle cleanser, exfoliate with AHAs or BHAs, apply scar treatments, moisturize, and always use sunscreen.





